Comparison Of XH connector & VH connector: Pros & Cons, Applications, Environments
For procurement managers and design engineers in consumer electronics, the choice between the XH connector and the VH connector has direct consequences on product reliability, cost, and production efficiency. This article provides an in-depth comparison of construction, performance, use cases, and environmental considerations. Since the terms XH connector and VH connector are often used interchangeably in informal discussions, we explain the actual technical distinctions and selection criteria. By understanding these factors, teams can reduce risk, improve sourcing efficiency, and ensure better alignment between engineering and supply chain priorities.
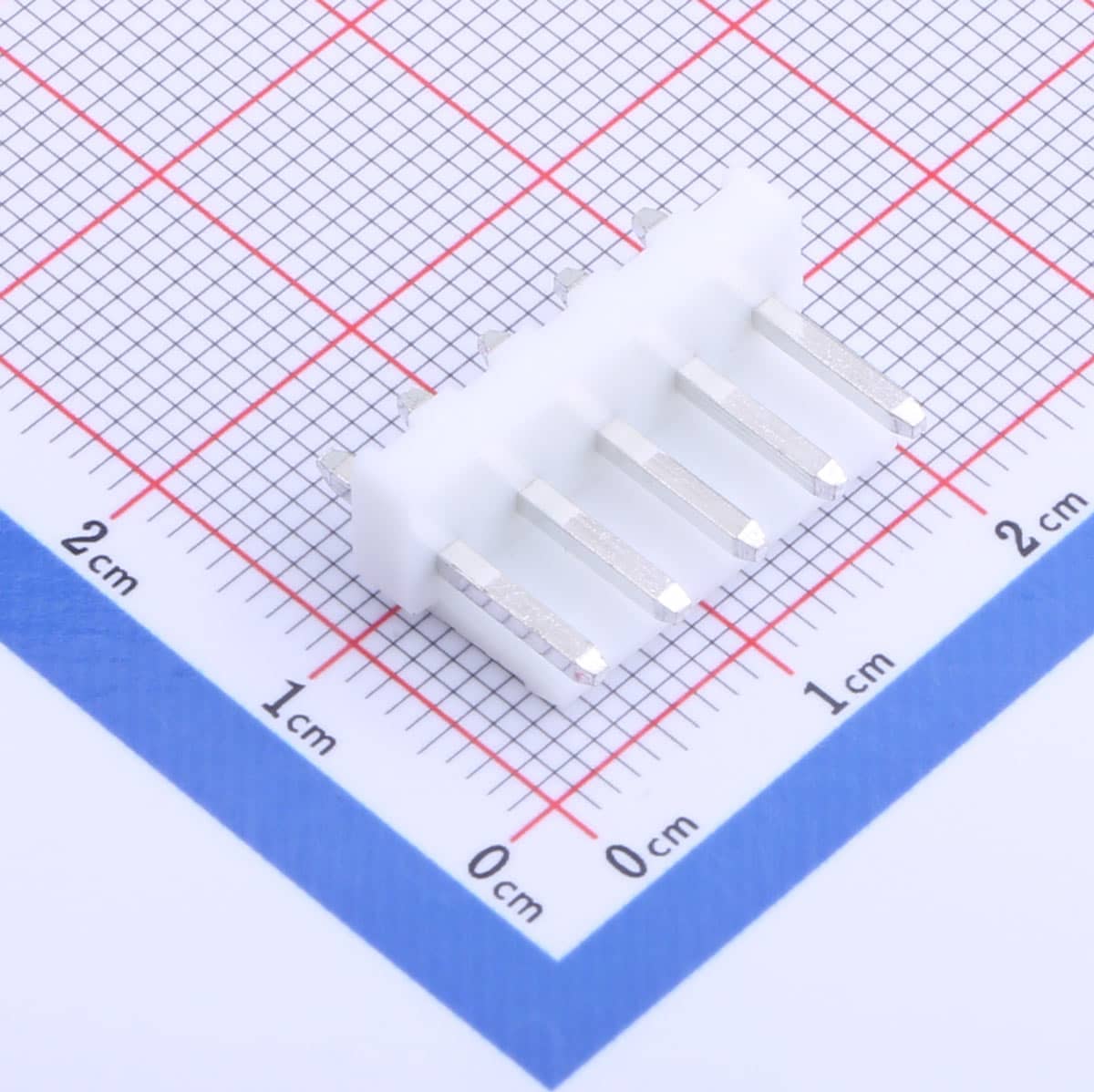
Overview of XH connector and VH connector
In electronic devices, wire-to-board connectors differ mainly by pitch, current capacity, and retention features. The XH connector is optimized for compact designs with limited space, while the VH connector targets higher power delivery and mechanical strength. Both are manufactured by reputable connector suppliers such as JST and are widely used in control boards, LED lighting, battery packs, and small motor applications. The XH connector saves board space and simplifies compact assembly, while the VH connector offers higher current handling and stronger locking mechanisms. These differences make them complementary solutions rather than interchangeable products.
Mechanical differences between XH connector and VH connector
Pitch and size
The most obvious difference between the XH connector and the VH connector is pitch. XH has a smaller pitch, making it ideal for high-density PCB layouts where every millimeter counts. VH has a larger pitch, which allows better creepage distance and easier routing for thicker copper traces. For designers, this translates into different trade-offs: compactness with XH or robustness with VH. Procurement teams often balance these options against board cost and assembly efficiency.
Retention strength
Retention force is another key factor. The XH connector relies on friction and polarization for secure mating, while the VH connector incorporates a stronger latch design to resist shock, vibration, or accidental disconnection. For handheld products or small consumer gadgets, XH provides sufficient reliability if strain relief is designed properly. For appliances, scooters, or industrial modules subject to vibration, VH is the safer choice.
Contact structure
The metal spring design and plating thickness vary across the two connector families. The XH connector uses a smaller contact surface suited for low-power signals, while the VH connector features thicker blades and larger contact areas, allowing higher current capacity. Procurement and quality teams should ensure that approved wire gauges and insulation types match the connector’s specifications to maintain consistent crimp strength and electrical performance.
Electrical performance: XH connector vs VH connector
Current and voltage rating
The XH connector is designed for lower current applications, typically used in signal transmission, sensors, and LED modules. In contrast, the VH connector can handle higher current loads, making it more suitable for motors, heaters, and power distribution nodes. The wider pitch of VH also provides better creepage and clearance distances, which is important in designs requiring compliance with safety standards. Engineers should consider both continuous and peak load requirements before finalizing their choice.
Thermal performance
Contact resistance and heat rise must be carefully reviewed during connector selection. The VH connector maintains lower temperature rise under higher current, whereas the XH connector can quickly approach its thermal limit if overloaded. Proper derating and realistic thermal modeling are essential in both cases, especially for sealed devices with limited airflow.
Pros and cons of XH connector and VH connector
Advantages of XH connector
Compact size conserves PCB area
Lightweight design reduces mechanical stress on solder joints
Widely available with stable pricing in global markets
Disadvantages of XH connector
Lower current rating compared to VH connector
Weaker latching force in vibration-intense environments
Narrow creepage distance limits high-voltage applications
Advantages of VH connector
High current capacity suitable for demanding loads
Strong latch mechanism ensures secure connections
Wider pitch simplifies compliance with safety standards
Disadvantages of VH connector
Larger footprint consumes more PCB space
Heavier and bulkier compared to XH connector
Higher insertion force can complicate automated assembly
Applications of XH connector and VH connector
The XH connector is widely used in LED drivers, small battery packs, fan headers, and compact control modules. Its low profile and fine pitch make it attractive for space-constrained designs. The VH connector is often specified in appliances, power tools, printers, and e-mobility devices where higher current and stronger retention are required. In consumer electronics, selecting between XH and VH often comes down to balancing space efficiency against power and durability. Companies that build both small wearable devices and larger household equipment often deploy both connector types across different product lines.
Environmental considerations
Reliability is heavily influenced by environmental exposure. The XH connector and VH connector families are generally rated for consumer environments, but extreme humidity, dust, and chemical exposure may require additional protection. For outdoor devices, material stability under UV and thermal cycling should be validated. In appliances exposed to cleaning agents, housing and plating materials must be checked for chemical compatibility. Documenting these assumptions early in the design process reduces risk of costly redesigns.
Compliance and references
Certification teams should rely on official data sheets and compliance documents when selecting connectors. Detailed specifications for the XH connector and VH connector can be found on the JST official website. UL recognition, IEC creepage rules, and RoHS/REACH compliance are critical considerations for procurement and engineering teams. Including connector choice in DFMEA ensures that risks such as partial insertion or terminal back-out are addressed early.
selection checklist
Determine continuous and peak current requirements
Confirm thermal rise and derating in the target enclosure
Balance pitch and PCB real estate constraints
Specify retention strength based on shock and vibration conditions
Define approved wire gauges and insulation for crimp quality
Validate assembly tooling and inspection processes
Secure supply chain alternates and stocking strategies
Conclusion
Choosing between the XH connector and the VH connector is not a matter of preference but of application. XH is the right solution when compactness, lightweight design, and moderate current are priorities. VH becomes the preferred option when higher current, stronger retention, and compliance margins are critical. By defining requirements carefully, documenting assumptions, and aligning procurement with engineering, companies can standardize their connector strategy and achieve consistent quality across product families.


Comments
Post a Comment