The Science Behind Wifi Antennas: Why Placement Matters More Than You Think
Understanding WiFi Antenna Placement
Proper WiFi antenna placement is essential for strong and reliable wireless connections. The position of your WiFi antenna directly impacts signal strength and coverage throughout your home or office. Ideally, place your WiFi antenna in a central location, away from thick walls and electronic devices that may cause interference.
Keep the WiFi antenna elevated, such as on a shelf or mounted on a wall, to help the signal travel further. For routers with adjustable antennas, angle them both vertically and horizontally to maximize coverage. Avoid placing the WiFi antenna near metal objects or appliances like microwaves, which can block or weaken the signal.
If your space is large or has multiple floors, consider using additional access points or mesh systems. Always check for dead zones and adjust the WiFi antenna placement as needed. Good WiFi antenna placement ensures faster speeds and fewer connection drops.
What Makes a WiFi Antenna Work?
A WiFi antenna works by transmitting and receiving radio frequency signals between your device and a wireless router. The WiFi antenna converts electrical signals from your device into electromagnetic waves, which travel through the air. These waves carry data, such as web pages or video streams, to and from the router.
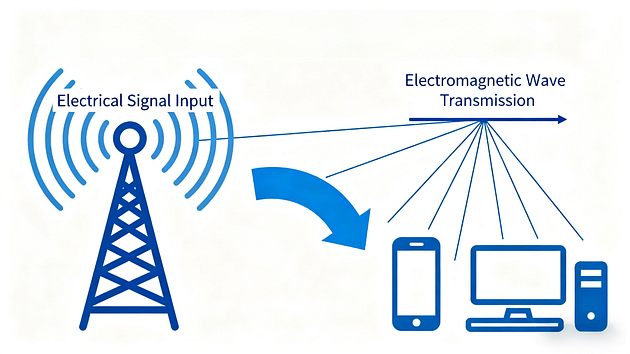
Most WiFi antennas are designed for specific frequency bands like 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, optimizing performance and range. The shape and size of the antenna — such as dipole or patch — affect how far and in which direction signals can travel. Internal WiFi antennas are hidden inside devices, while external ones can be adjusted for better signal strength.
Materials like copper or aluminum are commonly used in WiFi antennas for efficient signal transmission. Proper placement of a WiFi antenna is important to minimize interference from walls or other electronics. Overall, a WiFi antenna plays a crucial role in providing fast and stable wireless connections.
Types of WiFi Antennas Explained
WiFi antennas come in several types, each designed for specific coverage needs. The most common WiFi antenna is the omnidirectional antenna. This type distributes the wireless signal equally in all directions, making it ideal for home routers and office spaces.
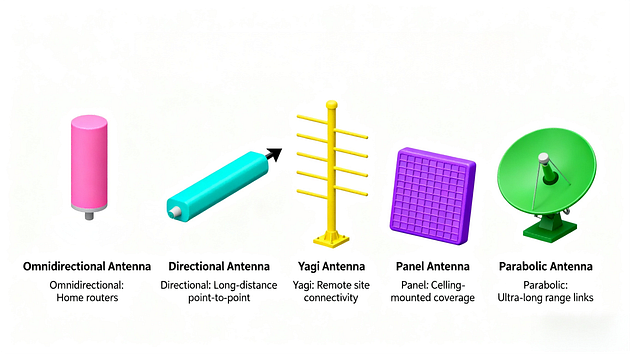
Another popular type is the directional WiFi antenna. These antennas focus the signal in a specific direction, greatly extending range and improving performance in targeted areas. Examples include Yagi and panel antennas, often used for point-to-point connections or long-distance links.
Dipole antennas are basic omnidirectional WiFi antennas found on most consumer routers. Patch antennas are flat, directional options suitable for mounting on walls to cover specific zones.
For outdoor use, parabolic WiFi antennas offer high gain and long-range capabilities. They are perfect for connecting buildings or reaching remote locations.
If you’re looking for high-performance, reliable Wi-Fi antennas, Kinghelm’s Wi-Fi antenna series offers a wide range of options, from omnidirectional to directional antennas, to meet the needs of various environments. Whether it’s for home or office use, choosing the right antenna can help optimize your network’s performance.
The Role of Radio Waves in Coverage
Radio waves are essential for wireless communication. They carry data between devices and access points. A WiFi antenna transmits and receives these radio waves, enabling connectivity.
The range and quality of a wireless network depend on radio wave strength. Obstacles like walls and furniture can weaken the signal. The design and placement of a WiFi antenna help overcome these challenges.
Different types of WiFi antennas, such as omnidirectional or directional, influence how radio waves spread. Omnidirectional antennas broadcast signals in all directions, while directional antennas focus signals in one direction for longer coverage.
Choosing the right WiFi antenna improves coverage and reduces dead zones. Proper antenna positioning ensures a stable and fast connection throughout the area. In summary, radio waves and WiFi antennas work together to deliver reliable wireless coverage.
Common Placement Mistakes and Their Impact
Incorrect WiFi antenna placement can significantly reduce your network’s performance. Placing the WiFi antenna behind large furniture or inside cabinets blocks signals, causing weak connectivity and frequent dropouts. Mounting the antenna too close to walls, metal objects, or electronic devices creates interference and signal reflection, further degrading your connection.

Positioning the WiFi antenna too low, such as on the floor, limits coverage and leaves dead zones in upper areas. Placing antennas together instead of at different angles fails to maximize signal spread. Many users also forget to position antennas vertically for optimal horizontal coverage.
These mistakes lead to slow speeds, unreliable connections, and frustrated users. Proper WiFi antenna placement is essential for a stable, high-speed wireless network throughout your home or office.
How Obstacles Affect Signal Strength
Obstacles like walls, doors, and furniture can weaken the signal from a WiFi antenna. Thick or dense materials, such as concrete or metal, block more of the signal than wood or drywall. Each time the signal passes through an obstacle, it loses strength.
WiFi antennas work best in open spaces with few barriers. When there are many obstacles, the signal may become slow or unreliable. Large appliances, like refrigerators, can also interfere with the signal.
Placing your WiFi antenna higher up or in a central location helps reduce the impact of obstacles. Try to keep the antenna away from electronic devices that might cause interference. By minimizing obstacles, you can improve your WiFi signal strength and coverage.
Tips for Optimal Antenna Positioning
Place your WiFi antenna in a central location within your home or office to ensure even signal coverage. Avoid placing the WiFi antenna near thick walls, metal objects, or large appliances, as these can block or weaken the signal.
Position the WiFi antenna vertically for most routers to maximize horizontal coverage. If your router has two antennas, angle one vertically and the other horizontally to cover multiple directions. Elevate the WiFi antenna on a shelf or high surface to reduce interference from furniture and obstacles.
Keep the WiFi antenna away from electronic devices like cordless phones and microwaves, which can cause signal interference. Adjust the direction of the WiFi antenna periodically to find the best coverage for your space.
Regularly check for software updates on your router to improve performance and compatibility. By optimizing your WiFi antenna positioning, you can enjoy faster speeds and a more reliable wireless connection.
Maximizing Your WiFi Performance
Maximizing your WiFi performance starts with the right placement of your WiFi antenna. Position your router and its WiFi antenna in a central, elevated location for the best signal coverage. Avoid placing the antenna near thick walls, metal objects, or electronic devices that can cause interference.
Upgrading to a high-gain WiFi antenna can boost your signal strength and extend your coverage area. Make sure the antenna is oriented vertically to improve horizontal coverage, or try different angles for multi-story homes. Keep your router’s firmware updated for optimal performance and security.
Minimize the number of devices connected at once to reduce congestion on your network. If possible, use dual-band routers and connect to the less crowded 5GHz band. By following these steps and optimizing your WiFi antenna, you’ll enjoy faster speeds and a more reliable connection throughout your home.


Comments
Post a Comment