What are DIP switches? What are DIP switches?
What is a DIP Switch?
DIP switches are dual in-line packages, which means that they consist of multiple switches within a single package. The user must manually move the actuator to activate or deactivate a different circuit. DIP switches are commonly mounted on PCBs or breadboards. They allow users to preconfigure electronic devices or toggle between different operating modes or settings.
Since the 1970s, DIP switches are electromechanical devices which allow manual modifications to be made to an electronic circuit. DIP switches are widely used in electronics because of their simplicity, flexibility and low price. These switches are available in many sizes, configurations and switching mechanisms.
The configuration options of the application will determine the number positions that the DIP switch has. DIP switches are available in a variety of configurations. Some can be operated by hand while others require the use of a screwdriver or special tool. Browse Kinghelm’s range of DIP switches.
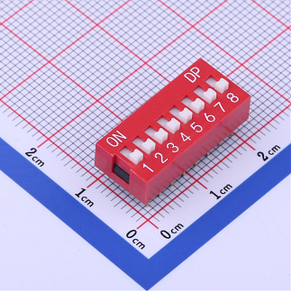
What are switch poles and throws?
In order to properly understand any switch, it is important to consider the poles and throws principle. The SPST switch is a single pole single throw switch that sits inside an electronic circuit. It can be closed to allow current to flow, or it can be opened and disrupt the flow of current.
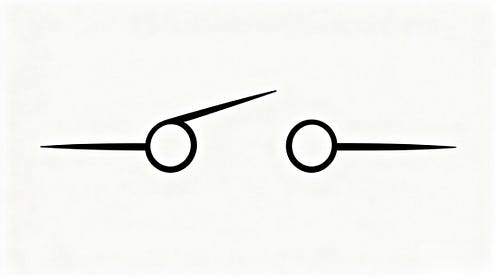
The SPDT switch allows current to flow in two different directions. Moving the actuator, in other words does not interrupt current flow. Instead it redirects the current into a new circuit branch.
Double pole, dual throw (DPDT), switches are used to control two circuits by using two linked switches. The other switch will also change position when the first one does. Each switch redirects current in a different direction within its circuit. This arrangement allows for multiple poles, multiple throws.
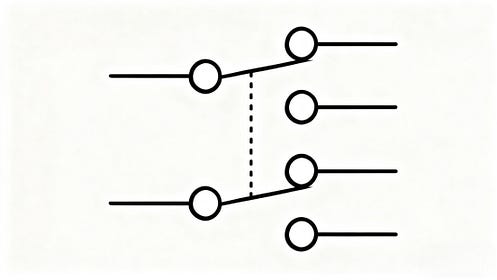
The number of switches that can be found in a single package depends on its application. It may range from one to sixteen positions. The eight positions of a common DIP package correspond to 256 binary codes which are equivalent to 1 byte.
DIP switches are available in different types.
DIP switches are available in many types. These include slide actuators piano actuators rotary actuators and more.
What are slide DIP switches?
Standard toggle switches are slide DIP switches. Each switch is a toggle switch with two positions: closed or open, also on/off (or 1/0). Slide DIP switches are available in three positions with a neutral position at the center and contacts on each end. These are typically configured to be on/off/on. DIP switches can be set to normally closed (NC) or normally open (NO). When actuated normally open switches complete the loop, while normally close switches interrupt the loop.
What are Piano DIP switches?
Slide DIP switches and piano DIP switches have many similarities. Piano DIP switches, however, are vertical and require an upward and downward motion.

What are Rotary DIP switches?
Rotary DIP switches change position when the user rotates the actuator in a circle. The output of the switch is determined by the amount of rotation. A DIP rotary switch with four pins of output can have up to 16 binary output configurations. The switch can be configured as an SPDT device with three or four throws per single pole.

DIP switches of Other Types
Other types of DIP switch include rocker actuators that operate like a swing. The switch mechanism moves between two positions. Lowering one side of actuator raises the opposite side. They are a variation on the basic toggle switch.
Specifications for Key DIP Switches
The datasheets of the manufacturer provide vital performance and specification details about each DIP. It is important to know this information when choosing the right DIP switch for an application. Here are some other specifications that you should consider, besides the obvious ones like the number of positions or actuator type:
Specification | The Typical Offering | Description |
Mounting Style | Surface or through hole | Surface mounted DIPs are ideal for PCBs, while through-hole versions are best used on breadboards |
Termination Style | Gull wing (angled gull wings), J-hook gull wings, PC pin and crimped pin | Different mounting options are available |
Voltage Rating | From 2.4 Vdc to 50Vdc | Maximum voltage across device. Voltage ratings list switching voltages and non-switching. The switching rating is used when the actuator moves from one position into another. Non-switching rating is when the actuator in a fixed position. It will be generally higher than switching rating |
Current Rating | From 10 to 200 mA | Maximum current through the device |
Pitch | 1.27, 2.54 or 5.08 mm | The distance from the center to the center of pins |
IP Rating | Rating or Non-Rating | DIP switches are resistant to moisture and dust. |
You should ensure that the DIP switch you choose meets your design’s requirements. If a DIP is used outside its specification, it can cause problems such as electrical arcing and self-welding. It could also compromise the device’s performance, or make it inoperable.
What are common DIP switch applications?
DIP switches are used in many applications. DIP switches have been used in IoT devices for years as a way to quickly preconfigure or reprogram an item before its implementation in a factory or smart home, thereby reducing downtime. DIP switches have many applications.
· Programming garage door openers
· Programming remote controls
· Configuration options for PC expansion cards and motherboards
· Easy user configuration allows for adding new devices to the IoT network.
· The configuration of industrial equipment can be checked without having to turn on the equipment
The conclusion of the article is:
DIP switches were first introduced to allow for easy changes in the characteristics of electronic systems. The DIP switch allows for configuration changes during manufacture or by the end user. The advent of software switches has reduced the use of these devices, but their ease of use and low cost make them a good choice for a wide range of electromechanical products.
Understanding DIP switches, and the different variations that are available, allows these applications to configure devices so they perform certain functions and can communicate with other matching devices.
The Key Takeaways
· DIP switches are electric manual switches that come in a format of dual-in-line for use on printed boards.
· DIP switches enable hardware-level configuration without requiring software updates or reprogramming.
· DIP switches are used in embedded systems, consumer electronic equipment, and industrial equipment. They can be used to set device modes, address devices, or enable/disable functions.
· To match circuit requirements, DIP switches are available in different pole-and-throw configurations such as SPST or SPDT.
· DIP switches have a reputation for simplicity, reliability and reusability, especially in settings with low frequency or non-volatile components.
· The key selection criteria for DIP switches include the number and type of positions (slide or piano), current rating and mounting style.
· Software solutions are replacing DIP switches in certain areas, but they remain essential in designs that require cost-sensitive functionality or do not require firmware.


Comments
Post a Comment